Transcriptomic analysis of model systems

Cross species transcriptome analysis can be a powerful tool for identifying rare disease genes. By looking at the transcriptome of a variety of species, including humans, it is possible to identify genes that are differentially expressed in the diseased state. This can help to identify both disease-causing genes and genes that are involved in the underlying processes.
RNA transcriptomics is the study of the transcriptome, which is the complete set of RNA molecules, including mRNA, lncRNA, piRNA, and asRNA, that are produced by a cell. Transcriptomics can be used to study the function of genes and to understand how the expression of genes is regulated. RNA-seq data analysis is the process of determining the function and structure of RNA molecules from high-throughput sequencing data, often termed Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). This data can be used to understand the underlying changes in gene expression, regulation, in relation to disease or treatment states.
Bulk RNA-seq has been the defacto gold standard used to investigate changes in gene expression, in tissues (including archived samples), cells, and model systems. RNA-seq data analysis involves the identification and characterization of differentially expressed gene or gene sets using a variety of different algorithms.
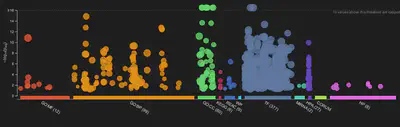
We use bioinformatics of RNA-seq data to explore the functional relationships between the changes in feature (gene/transcript) expression between conditions. Initially modelling and identifying expression of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) allows us to test numerous hypothesis as to what may be driving these changes. Using enrichment and over-representation analysis allows us to furhter link observed changes between conditions to the underlying molecular defects controlling such changes.
Using various model systems; including zebrafish mutants, 3D retinal organoid optic cup vesiciles, patient cell lines, iPSC stem cells and standard cell lines, I am interested in how genetic variants in eye disease functionally come about. These diseases include:-
- CRB1-related Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) and Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
- Ushers Syndrome
- MAC (Microphthalmia, Anophthalmia and Coloboma).
- RDH12-related retinitis pigmentosa
- Myopia

Using an analagous approach with the Genomics England 100,000 Genomes rare disease dataset (GEL), I utilise the RNA-seq data to identify potential novel causative genes from variants of uncertain significance (VUS) in specific patient cohorts.
Bioinformatics is used to term a field of biology that deals with the application of computer techniques to the management and analysis of biological data.


